
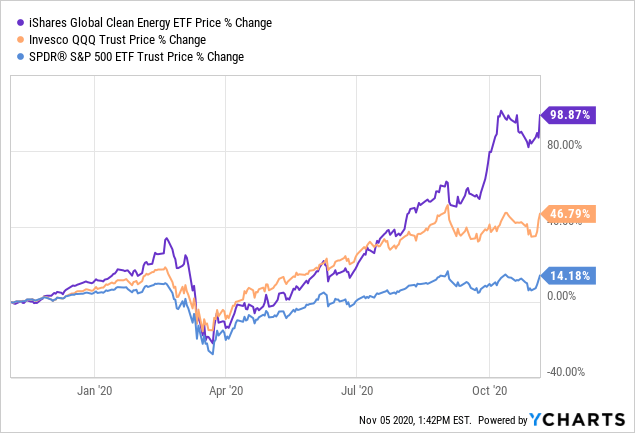
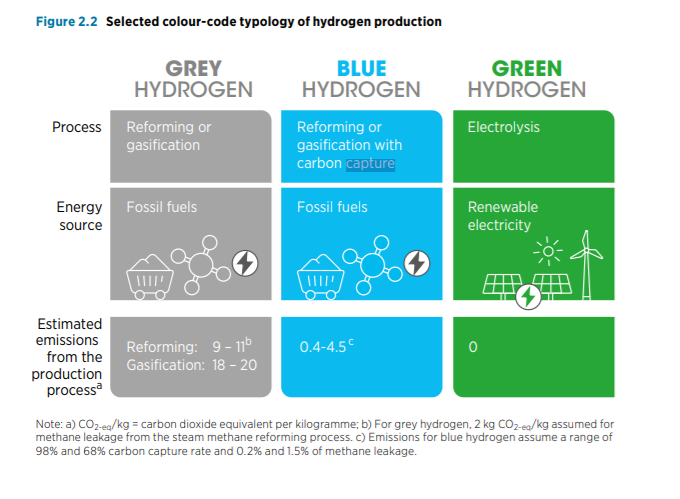
Renewable energy resources come in many forms and may be classified based on their development potential, country of origin, and potential urban or rural customer base. Policies may decide to differentiate between resources with established markets and those that are new or emerging. These differences may also apply when deciding on how to apply renewable energy resources to urban settings.
Water
Water is a renewable resource and can be used in multiple ways. Its worth as a resource will depend on how many people use it, and how valuable the ecosystem regards it. As human appropriation increases, the value of water declines and ecological services decrease. The value of water as a renewable resource is capped at a point, or "peak ecological water" in ecological terms, where the value of the ecosystem is equal to or less than the value of water as a resource to humans.
Earth's oceans are home to 0.3 million cubic miles of liquid. This represents 97% of the total water on Earth. The majority of this water is saltwater, with more than one gram of dissolved solids per liter. Saltwater isn’t suitable for most people and terrestrial animals. Freshwater on the other hand has a low amount of dissolved materials. Freshwater, however, is the primary resource for human consumption. The amount of salt in freshwater tends to be much lower.
Biomass
Biomass can be used to produce heat or electricity. It is a renewable resource that can be burned. It is an attractive resource because of its versatility. It is used in wood heating systems. Sometimes, it can even be used in combined power units to create electricity. This makes biomass a viable option to help the UK reach its 2020 emission reduction targets.
Biomass has the advantage of being a renewable resource. It will be there for ever. It can also be a very costly resource. It can cost as high as $100,000 to process algae. This makes it out of reach for most developing countries. Even though it comes at a high price, biomass is an affordable renewable resource that can be quickly regenerated. It can also be harvested from municipal solid waste.
Hydropower
Hydropower, one of the oldest renewable resources, is also the most reliable. This natural resource offers many benefits to the grid and communities. Hydropower is also an eco-friendly resource. The best alternative source for energy is hydropower. Click the button below for more information about hydropower.
Hydropower facilities harnesses the energy of moving waters by placing turbines in rivers or lakes. The water then converts the energy into electricity, which is fed into the electric grid. Hydroelectric plants are more environmentally friendly than other forms of energy generation. Hydroelectric plants are completely renewable because the water used is always replenished.
Geothermal power
Geothermal power is a natural energy source that comes from hot water reservoirs deep in the earth. There are many industries that use geothermal energy. It is also used to reduce the consumption of fossil fuels and greenhouse gas emissions. This explainer gives an overview on traditional and next generation geothermal technologies and highlights the advantages and challenges associated with increased geothermal use.
Flash steam plants are the most popular type of geothermal power station. They produce electricity by deep-sea water conversion. The water is then extracted, and the steam is converted into electricity to turn a turbine. This steam is then injected back in the earth and repurposed. A second type of geothermal power plant is called a dry steam plant, and it uses the natural steam rising from underground to run a turbine generator.
Solar energy
Solar energy is one renewable resource that can be used in a wide variety energy applications. It can be used to create electricity at large-scales using solar panels or to power smaller devices such as LEDs. It can generate hundreds of megawatts and require millions of panels to cover large areas. Tracking systems that are dedicated to solar panels allow them to track the sun and increase their efficiency. Concentrated sun power, which makes use of the heat from sunlight to heat a fluid and create electricity, is another option.
The average solar energy density outside the atmosphere is about 1,300 Watts per square meter. Although most of the energy is reflected back into the atmosphere, a squaremeter will still collect approximately 4.2 kilowatts of solar power per day. This is equivalent to the energy output of nearly a barrel of oil every year. The Sahara Desert receives six kilowatt hours of solar energy per square foot. Photovoltaic panels or concentrating solar power plants convert the energy into electricity.